Build from Source
WARNING
Please note that you should not switch between running unreleased code from git branches and official releases of rotki on the same data set, as unreleased code does not provide guarantees around forward-compatibility of data schemas etc.
Prerequisites
Before starting, ensure you have the following installed:
- Git
- Python 3.11.x
- uv (Python package manager)
- Node.js
- pnpm
Downloading source
This guide assumes you want to use Git to clone the project into a development directory; if you prefer to download the source from GitHub as a zip, you can do that instead.
- Fork the relevant rotki branch into your own GitHub account.
- Open a terminal (Command Prompt / PowerShell prompt) in your root development directory (the parent directory of where you will place your rotki development directory).
- Clone your forked project into the local directory where you want to build rotki (e.g., if you forked the rotki/develop branch, you might clone into
c:\dev\rotki-develop).
In your local rotki development directory, you should have all the files as they appear in the GitHub page for the rotki branch you chose to download/clone.
Backend setup for Linux
Set Up Python Environment
Install uv, the modern Python package manager:
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | shThen set up the development environment:
# Install all dependencies including dev and lint groups
uv sync --group dev --group lintFollow the Frontend setup to complete the setup.
Backend setup for macOS
The tl;dr version is:
- Use a virtual environment with Python 3.11.x.
- Confirm
pip(pip3) is installed correctly and up to date.
Install Homebrew first if not installed yet.
Set Up Python Environment
Install uv, the modern Python package manager:
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | shThen set up the development environment:
# Install all dependencies including dev and lint groups
uv sync --group dev --group lintFollow the Frontend setup to complete the setup.
Backend setup for Windows
Dependencies
- Install Python 3.11 (64-bit version for 64-bit Windows).
- Ensure Python is in the Path variable. If not:
- Go to Control Panel -> System -> Advanced system settings -> Advanced (tab) -> Environment Variables...
- Under "System Variables," open the "Path" variable and ensure both the root Python directory and the
Scriptssubdirectory are included. - If not, add them by clicking "New" and then "Browse" and locating the correct directories.
- By default, the Windows MSI installer places Python in the
C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Local\Programs\directory.
- Test Python installation by opening a command prompt and typing
python. The Python CLI should run, showing the Python version you installed. PressCTRL+Z, then Enter to exit.Note: In newer versions of Windows, typing "python" may open the Windows Store. Fix this by opening "App execution aliases" (search for it via Windows Search) and toggling off the aliases for python.exe and python3.exe.
- Install uv, the modern Python package manager. Open PowerShell as Administrator and run:sh
powershell -c "irm https://astral.sh/uv/install.ps1 | iex" - Install Microsoft Visual Studio build tools with the "Desktop development with C++" workload.
Set Up Python Environment
- Open a terminal (Command Prompt / PowerShell prompt) in your root development directory.
- Ensure you are in the directory where you downloaded/cloned the rotki source.
- Install all dependencies:sh
# Install all dependencies including dev and lint groups uv sync --group dev --group lint - Download miniupnpc for Windows and copy
miniupnpc.dllto your virtual environment'sLib > site-packagesdirectory. Locate this directory using:shuv run python -c "import site; print(site.getsitepackages()[0])"
Then follow the Frontend setup to complete the setup.
To ensure rotki backend works, try starting it:
uv run python -m rotkehlchenThis should greet you with the message:
rotki REST API server is running at: 127.0.0.1:5042Frontend setup
Make sure you have Node.js installed. You can check https://nodejs.org/en/download/package-manager for more information.
Installing PNPM
Check the required PNPM version in frontend/package.json under the packageManager key. For example, if it says:
{
"packageManager": "pnpm@10.0.0"
}It means you need to have pnpm version 10.0.0 installed. To check the current version of pnpm you have, run:
pnpm --versionIf you are on an older version of pnpm, you can install it by:
corepack enable pnpmThis will automatically use the version specified in packageManager.
Install Node.js Dependencies
cd frontend
pnpm install --frozen-lockfileRunning rotki
Start the application from the frontend directory:
pnpm run devFor non-Electron development:
pnpm run dev:webPackaging
To package the application for your platform, you need to install the packaging dependencies and run the packaging script:
# Install packaging dependencies
uv sync --group packaging
# Run the packaging script (works on all platforms)
uv run python ./package.py --build fullNix
You can use the Nix package manager to start rotki development. Create flake.nix in the root of the project and copy the following into it:
{
description = "rotki project with uv-managed virtualenv";
inputs = {
nixpkgs.url = "github:NixOS/nixpkgs/nixos-24.05";
nixpkgs-unstable.url = "github:NixOS/nixpkgs/nixpkgs-unstable";
flake-utils.url = "github:numtide/flake-utils";
};
outputs = { self, nixpkgs, flake-utils, ... }:
flake-utils.lib.eachDefaultSystem (system:
let
pkgs = nixpkgs.legacyPackages.${system};
python311 = pkgs.python311;
nodejsWithPython = pkgs.nodejs.override { python3 = python311; };
nodePackages = pkgs.nodePackages.override { nodejs = nodejsWithPython; };
pnpmWithPython311 = nodePackages.pnpm;
devShell = pkgs.mkShell {
name = "rotki-dev";
buildInputs = [
pkgs.gcc
pkgs.stdenv.cc.cc.lib
pkgs.bash
pkgs.git
pkgs.lzma
pnpmWithPython311
python311 # interpreter uv will bind into the venv
pkgs.uv # blazing-fast venv + installer
];
shellHook = ''
# Installs deps and auto-creates .venv if missing
uv sync
# Install frontend dependencies
cd frontend
pnpm install
cd ..
'';
};
in { inherit devShell; });
}Then execute the following command to let Nix build the entire environment where you can start rotki development:
nix developFrom this point onward, start backend/frontend:
cd frontend
pnpm run dev:webDocker
To build Docker image from source using Dockerfile:
docker build -t rotki .Troubleshooting
anyapi-ms-win-crt-runtime missing
If you get anyapi-ms-win-crt-runtime-l1-1-0.dll is missing error when running Python, follow this guide to resolve it.
Microsoft Visual C++ 14.0 is required
If you get:
building 'gevent.libev.corecext' extension
error: Microsoft Visual C++ 14.0 is required. Get it with "Microsoft Visual C++ Build Tools": https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/downloads/Then go here and get the Microsoft Visual Studio build tools and install them. The specific parts of the tools that need to be installed can be seen in this Stack Overflow answer.
You also need to add them to the path. The tools were probably installed here: C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2017\BuildTools\Common7\Tools Environment variable should be: VS140COMNTOOLS
Blank screen when running the dev server
If you get a blank screen on electron when starting the development server check the console for any messages like the following:
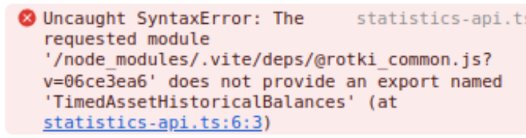
If you see any syntax error message like the one above, go to Help and press Clear Cache. After that go to the View menu and press Force Reload.
This should resolve your issue.
If the issue persists, try following the frontend troubleshooting steps.
